

Led by the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the team—which included researchers from China, Australia, Spain, and the United States—conducted multidisciplinary archaeological investigations at the Xigou site in the Danjiangkou Reservoir region of central China. Their work yielded evidence of sophisticated stone tool technologies dating from 160,000 to 72,000 years ago, revealing that hominins in the region were far more innovative and adaptable than previously thought.

A collaborative team led by Profs. FENG Wei and ZHAO Yan from the Institute of Biophysics has systematically elucidated the conformational dynamics of the AP-4 core complex and uncovers the molecular mechanisms governing its membrane recruitment and cargo transport by combining cryo-electron microscopy, biochemical analyses, and cellular assays.

Researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed how a network of proteins works together to regulate iron balance throughout the whole plant, which fills the gap in understanding how plants manage this essential nutrient.
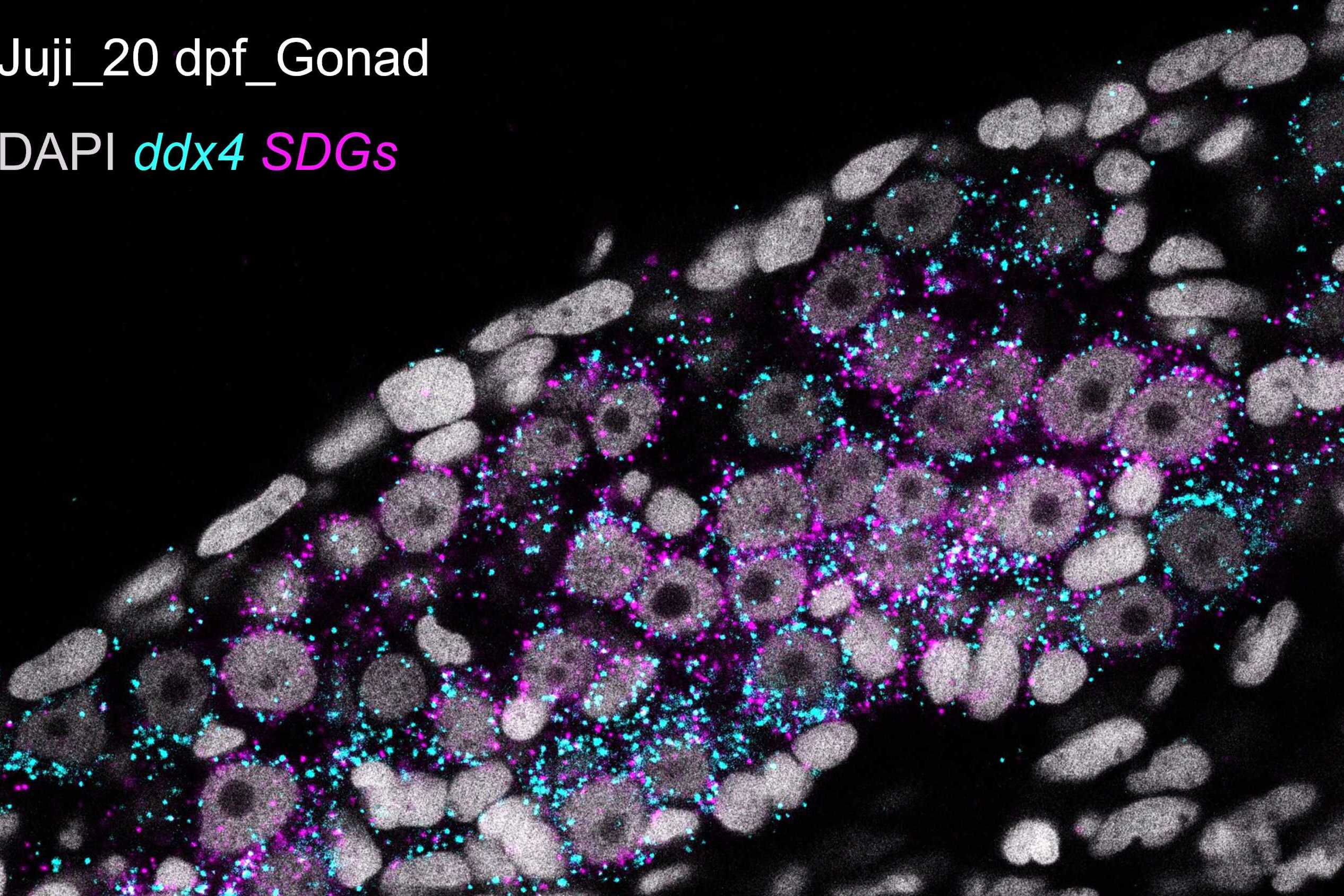
A team led by Prof. SUN Yonghua from the Institute of Hydrobiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences constructed a transgenic Juji line, Tg(ddx4:EGFP-UTRddx4), which enables continuous labeling of the germ cell lineage across all developmental stages, demonstrating that the Juji is an excellent model for studying germ cell development and gonadal differentiation.
Research teams led by Profs. WANG Qianfei and LIU Zhaoqi from the China National Center for Bioinformation, a research center affiliated to the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the Children's Hospital of Soochow University, analyzed transcriptome sequencing data from 702 pediatric AML patients. The team identified sequence-dependent ribonucleic acid (RNA) splicing abnormalities in roughly 36% of the cases.
Researchers from the Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science (Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology) and Tongji University identified a fibrous-layer resident subpopulation of P-SSCs labeled by Angptl7. They found that these cells are crucial for bone fracture repair by mediating endochondral ossification, but exhibit minimal osteogenic capacity during postnatal bone development and maintenance.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

